Date: 2025-12-17
Let's talk about a quiet revolution in electronics packaging. For decades, circuit boards were rigid, flat, and confined to boxy enclosures. But what if your product needs to fit into a curved space, survive constant motion, or simply be impossibly thin and light? That's where flex circuit assembly comes in—a specialized skill that brings functionality to the most demanding and innovative designs.
For any manufacturer developing cutting-edge wearables, medical devices, or compact consumer electronics, understanding flex circuits is no longer optional. It's the key to unlocking form factors and reliability standards that rigid boards can't touch.
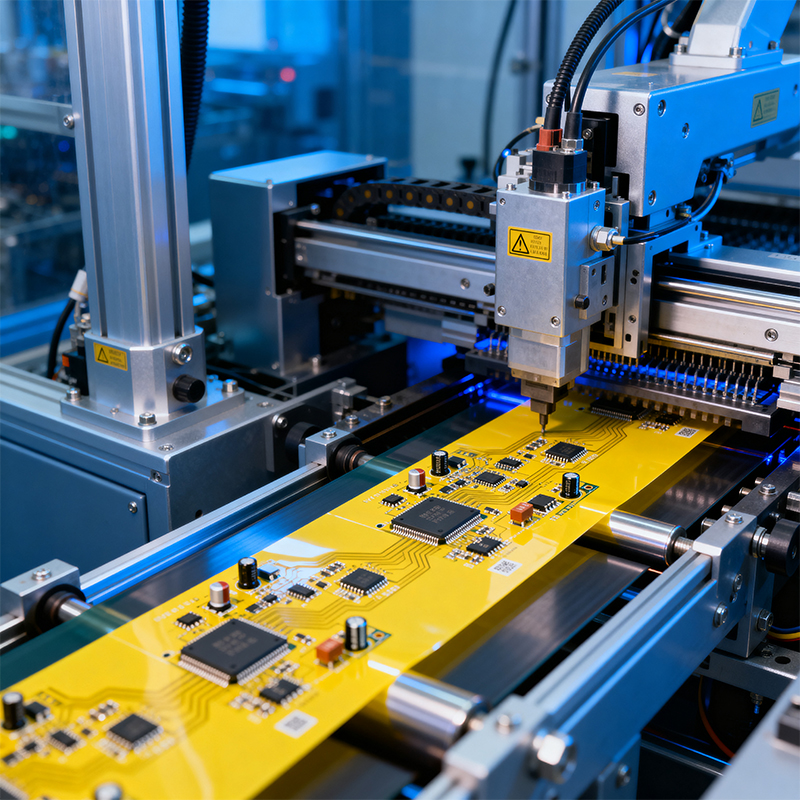
At its core, flex circuit assembly is the process of populating and soldering electronic components onto a flexible printed circuit (FPC or flex PCB).
The Foundation: The Flex Circuit. Unlike traditional FR-4 fiberglass boards, flex circuits are made from thin, flexible polymer films like polyimide. Delicate copper traces are etched onto this film, creating a circuit that can bend, fold, and flex repeatedly without breaking. Think of it as the difference between a sheet of glass and a sheet of durable plastic.
The Process: The Specialized Assembly. Putting parts on this flexible foundation is where the expertise lies. It's not just "SMT on a bendy board." It requires handling a substrate that doesn't stay flat, managing unique thermal properties, and ensuring connections survive dynamic stress.
So why go through the extra effort? The benefits of flex circuit assembly solve fundamental design challenges:
1. Enabling Ultimate 3D Packaging and Space Savings.
This is the biggest driver. A flex circuit can be folded, creased, or rolled to fit into tight, irregularly shaped spaces—saving up to 60% or more in weight and space compared to rigid boards and wiring harnesses. It's why your smartphone camera module connects to the mainboard, or how a smartwatch fits all its electronics into a curved case.
2. Achieving Unmatched Dynamic Flexibility and Reliability.
For parts that move continuously, a rigid board is a liability. Flex circuits are designed to bend millions of times. This is critical for:
Hinge assemblies in laptops and flip phones.
Moving print heads in industrial printers.
Robotic arms and joints where wiring would fail.
3. Improving System Reliability and Performance.
By replacing multiple rigid boards, connectors, and cables with a single, integrated flex assembly, you drastically reduce potential points of failure. Fewer connectors mean better signal integrity for high-speed data and increased overall system reliability.
4. Enhancing Durability in Harsh Environments.
High-quality polyimide materials offer excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and radiation, making flex assemblies ideal for under-the-hood automotive applications, down-hole drilling equipment, and aerospace.
Successfully assembling flex circuits requires conquering unique hurdles that can trip up standard PCBA shops:
Handling a Floppy Substrate: The board doesn't stay put. It requires specialized carriers, fixtures, and pallets to hold it perfectly flat and stable during screen printing, pick-and-place, and soldering.
Precision Thermal Management: Polyimide and thin copper have different thermal mass and expansion rates than FR-4. Extremely precise control of reflow oven temperatures is needed to prevent warping, delamination, or "potato-chipping" of the board.
Stress Management on Solder Joints: Any point where the flex bends near a component creates stress on the solder joints. Techniques like strategic stiffener application and protective epoxy coatings (corner bonding/edge sealing) are essential for long-term reliability.
Delicate Material Care: The thin gold or ENIG finishes on contacts are easily scratched. The entire process, from kitting to final packaging, demands a heightened level of cleanliness and material handling care.
You'll find expertly assembled flex circuits at the heart of innovation:
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, cameras, VR headsets.
Medical Devices: Hearing aids, implantable devices, endoscopic probes, wearable monitors.
Automotive: LED lighting arrays, infotainment systems, sensor modules around the engine.
Industrial & Aerospace: Compact sensors, robotics, guidance systems, satellites.
Mastering flex circuit assembly requires more than just a standard SMT line; it demands specialized processes, tooling, and a deep understanding of material science. At Kaboer, our factory in Shenzhen is equipped to handle these precise challenges.
We understand that a flex circuit isn't just a component; it's often the critical, enabling skeleton of a cutting-edge product. Our process is built around the care and precision these assemblies demand—from custom fixtures that ensure perfect placement to rigorously controlled thermal profiles that protect the integrity of the flexible substrate. For product developers pushing the boundaries of size, shape, and durability, partnering with an assembler who respects the nuances of flex technology is a critical step toward success.
Kaboer manufacturing PCBs since 2009. Professional technology and high-precision Printed Circuit Boards involved in Medical, IOT, UAV, Aviation, Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Control, Artificial Intelligence, Consumer Electronics etc..