Date: 2025-12-20
Electrical parts assembly - it's the critical, behind-the-scenes process that breathes life into your electronic designs. For manufacturers bringing products to market, mastering this stage means the difference between a brilliant concept and a reliable, market-ready device. Let’s break down what it truly entails and how to get it right.
Gone are the days of simple soldering irons and manual labor. Today, electrical parts assembly is a high-tech symphony of precision robotics, advanced materials science, and rigorous process control. It’s where your PCB design meets the physical world, transforming a board full of pads into a functional system.
The stakes are high: a single poorly placed component or a weak solder joint can lead to field failures, costly recalls, and damaged reputations. Understanding the assembly landscape is no longer optional—it’s a core business competency.
How does a bare board become a smart device? Here’s the journey:
Step 1: The Prep Work (Where Success is Built)
Before any machine starts humming, critical groundwork happens. This includes a thorough Design for Manufacturability (DFM) check—where an experienced engineer reviews your files to spot potential production nightmares before they occur. Simultaneously, all components are verified for availability, authenticity, and compatibility.
Step 2: Applying the "Glue" (Solder Paste Printing)
A laser-cut stainless steel stencil aligns perfectly over the board. Solder paste—a mixture of tiny solder balls and flux—is precisely pressed through its openings onto every pad. The accuracy here is astounding, often within ±0.025mm. This step is deceptively simple but utterly crucial; too much paste causes shorts, too little causes weak connections.
Step 3: Robotic Precision (Component Placement)
This is where automation shines. High-speed pick-and-place machines, guided by sophisticated vision systems, pick components from reels, trays, or sticks and place them at speeds of tens of thousands per hour. They handle everything from minuscule 01005 resistors (smaller than a grain of sand) to large, complex processors.
Step 4: Making it Permanent (Reflow Soldering)
The board travels on a conveyor through a multi-zone reflow oven—a precisely controlled heating tunnel. The temperature profile is meticulously crafted to melt the solder paste without damaging sensitive components, forming solid, reliable electrical and mechanical bonds as it cools.
Step 5: The Eagle-Eyed Inspection
No process is perfect, which is why inspection is non-negotiable. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems use high-resolution cameras to check for missing, misaligned, or tombstoned components. For hidden connections under chips (like BGAs), X-ray machines peer inside to verify solder joint integrity.
Step 6: The Final Checks (Testing & Validation)
Finally, the assembled board must prove it works. Testing can range from a simple power-on check to comprehensive In-Circuit Test (ICT) or Functional Test that validates performance against every specification.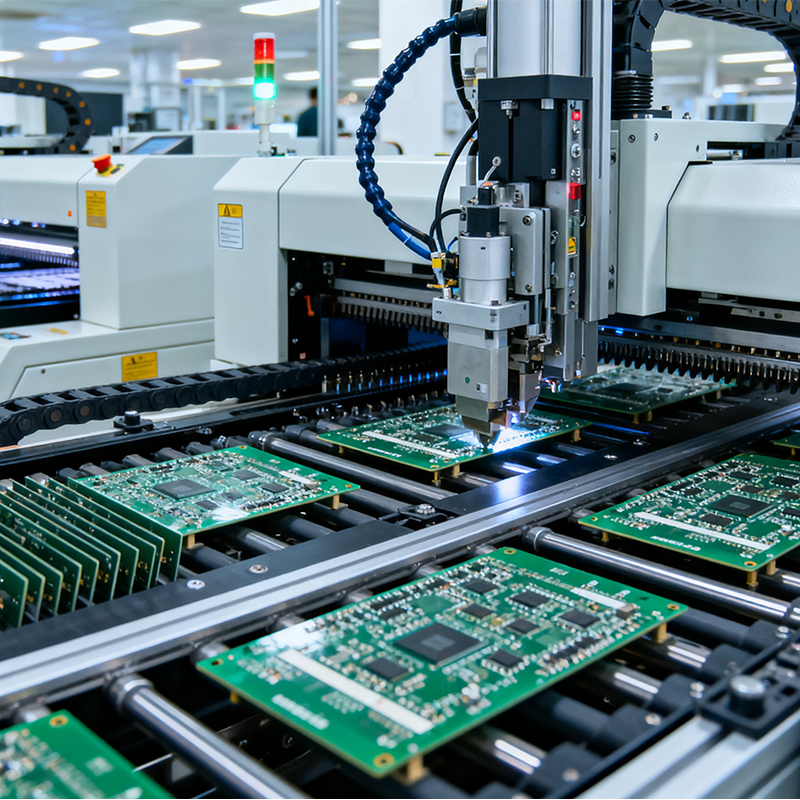
Even with the best plans, challenges arise. Here are the big ones:
The "Black Market" Component: Counterfeit parts are a rampant, costly risk. They fail unexpectedly and can jeopardize entire product lines. The solution? Partner with assemblers who have robust, traceable supply chains and rigorous incoming inspection protocols.
The Design Blind Spot: A board that works in simulation can still be a nightmare to build. Components too close together, impossible-to-inspect areas, or unrealistic thermal demands will grind production to a halt. This is where a manufacturer’s DFM feedback is worth its weight in gold—it translates a theoretical design into a manufacturable product.
The "Oops" in the Process: Solder bridges, cold joints, or misplaced components happen. The goal isn’t perfection, but catching errors early. A strong assembly partner layers multiple inspections (SPI after printing, AOI after placement, X-ray after reflow) to catch defects at the stage where they’re cheapest to fix.
The Scaling Cliff: A perfect 10-piece prototype run doesn’t guarantee a smooth 10,000-unit production. Processes, fixtures, and even component batches need to be optimized for volume. Your assembler should guide this transition, not just execute orders.
You can have a world-class design, but its success is ultimately forged on the assembly line. The right partner brings more than just machines—they bring process intelligence.
This is the space where Kaboer operates. Based in Shenzhen at the heart of global electronics manufacturing, we’ve built our expertise on solving these real-world problems for international brands.
What does this look like in practice?
It’s our engineers proactively flagging a potential thermal issue in your layout before the first board is built.
It’s our sourcing team leveraging deep local networks to secure genuine components and manage supply volatility.
It’s our production floor utilizing a closed-loop process where inspection data automatically fine-tunes the solder paste printer, preventing defects from repeating.
We provide a seamless bridge from prototype to volume production, ensuring that what works in your lab can be built reliably, efficiently, and at scale in our factory. Think of us as an extension of your manufacturing team, focused on turning your electrical parts assembly from a complex challenge into a predictable, controlled advantage.
The future of assembly is connected and intelligent. Imagine production lines where machines self-correct based on real-time inspection data, where AI predicts a component feeder will run empty before it happens, and where you can track your batch’s quality metrics from halfway across the globe. This level of transparency and control is becoming the new standard for reducing risk and time-to-market.
Electrical parts assembly is the decisive phase where design intent meets manufacturing reality. In a market where quality and reliability are non-negotiable, the depth of your assembly partner’s expertise is a direct competitive advantage. It’s not just about putting parts on a board—it’s about building the foundation of your product’s reputation.
Kaboer manufacturing PCBs since 2009. Professional technology and high-precision Printed Circuit Boards involved in Medical, IOT, UAV, Aviation, Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Control, Artificial Intelligence, Consumer Electronics etc..