Date: 2025-12-31
What is a Printed Wiring Board (PWB)?
Think of any electronic device you own. Its functionality hinges on a central, often green, board inside. This board is the Printed Wiring Board (PWB), also universally known today as a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). The term “PWB” is an older, sometimes industry-specific term that emphasizes its core function: it is the physical platform that provides the mechanical support and the electrical connections for all components.
At its simplest, a PWB/PCB is a flat sheet of insulating material (like fiberglass) with thin lines of copper “wiring” etched onto its surface in a specific pattern. These copper traces form the electrical pathways, replacing the need for a tangled mess of individual wires. Components like chips, resistors, and capacitors are then soldered onto designated connection points on this board, creating a complete, functional circuit.
While “PCB” is the more common contemporary term, “PWB” is still used, particularly in contexts stressing the board’s wiring function or in certain mature industries.
How is a PWB Made? A Simplified Look
The creation of a PWB is a precise, multi-step process:
Design & Layout: An electrical schematic is translated into a physical wiring layout using specialized software.
Printing the Pattern: This layout is printed onto the board, marking where copper should remain.
Etching: The board is treated chemically to remove all unwanted copper, leaving only the desired conductive “wires” or traces.
Layering & Lamination: For multi-layer boards, several single-layer boards are stacked, aligned, and fused together under heat and pressure.
Drilling & Plating: Holes are drilled for mounting components or creating connections between layers. These holes are then plated with copper to make them conductive.
Applying the Finish: A protective solder mask (usually green) is applied over the copper to prevent short circuits, and a silkscreen layer is added for labels and indicators.
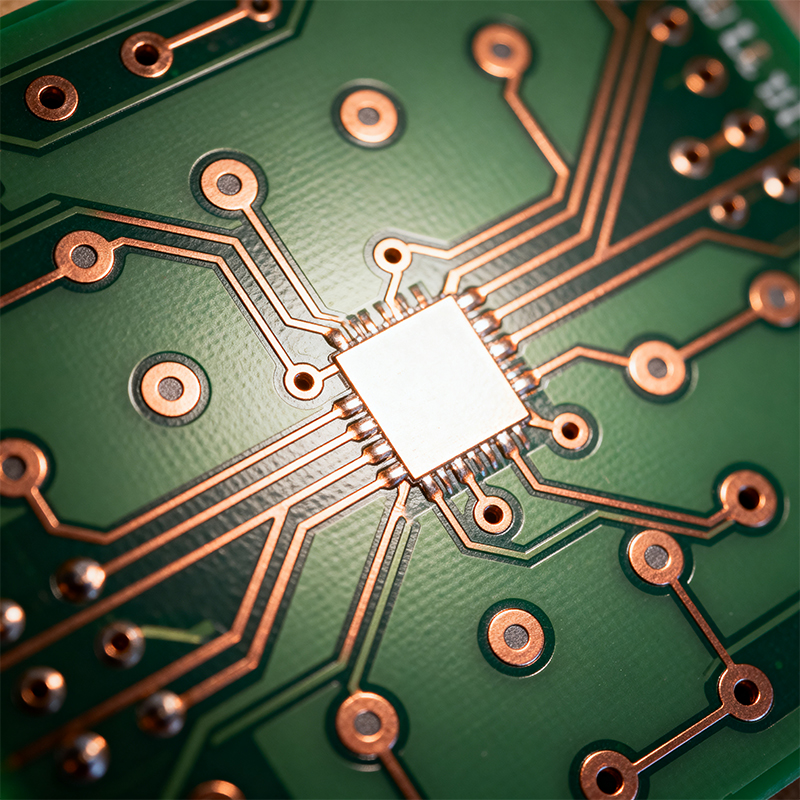
Types of PWBs/PCBs
PWBs/PCBs come in several forms to suit different applications:
Single-Sided: Wiring on only one side. Simple and low-cost for basic circuits.
Double-Sided: Wiring on both sides, connected by plated-through holes. Offers greater complexity in a compact space.
Multi-Layer: Three or more conductive layers laminated together. Essential for complex, high-performance devices like smartphones and servers.
Rigid vs. Flexible: Most boards are rigid, but flexible PWBs use bendable materials for innovative, space-saving designs.
Material Choices: Standard boards use FR-4 fiberglass. High-frequency or high-heat applications may require advanced materials like Rogers or metal-core boards for superior heat dissipation.
Why Quality in the Foundation Matters
The PWB/PCB is not just a passive carrier; it is the foundation of your product’s performance and reliability. A poorly designed or manufactured board can lead to critical failures:
Signal Integrity Issues: Trace design affects the speed and clarity of electrical signals. Poor design can cause interference, data corruption, or device malfunction.
Thermal & Mechanical Failure: Inferior materials or improper construction can lead to overheating, delamination (layers separating), or broken traces from physical stress.
Manufacturing Defects: Shorts, opens, or misaligned layers from substandard fabrication will doom the final assembly before a single component is added.
Navigating PWB/PCB Manufacturing with a Partner
For overseas electronics manufacturers, sourcing high-quality, reliable boards involves navigating design complexity, material selection, and rigorous quality control. This is where partnering with an expert becomes a strategic advantage.
Kaboer: Your Expert Partner for the Foundation
At Kaboer, based in the electronics manufacturing hub of Shenzhen, China, we understand that a successful build starts with a perfect foundation. Our vertically integrated services extend to expert PWB/PCB fabrication and sourcing.
How We Ensure a Superior Foundation for Your Build:
Design for Excellence (DFX) Review: Our engineering team doesn’t just receive your Gerber files. We perform a proactive Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Design for Assembly (DFA) analysis. We identify potential issues in trace width, spacing, hole sizes, and layer stack-up that could affect yield, performance, or assembly, providing feedback to optimize your design before production.
Material Guidance & Sourcing: We advise on the most suitable board material (FR-4, high-Tg, aluminum-core, etc.) based on your electrical, thermal, and budget requirements. Leveraging our Shenzhen location, we source high-quality laminates from trusted suppliers, ensuring material consistency and traceability.
Precision Fabrication & Stringent Quality Control: We manage relationships with highly capable, certified fabrication partners. Every batch of boards undergoes strict incoming inspection, including checks for trace integrity, insulation resistance, and solder mask alignment. We validate the foundation so your assembly process proceeds flawlessly.
Seamless Integration with PCBA: As a full-service PCBA provider with our own factory, we manage the entire flow. From PWB fabrication and component procurement to precise SMT assembly and testing, you have a single point of contact and responsibility. This integration eliminates communication gaps and ensures your board design is perfectly optimized for our assembly lines.
Conclusion
The Printed Wiring Board (PWB/PCB) is the critical, often overlooked, backbone of your electronic product. Its quality directly determines the ceiling for your device’s performance and reliability. Choosing a partner who provides expertise at this foundational level is not just a procurement decision—it’s a quality decision.
Ready to build your next product on a foundation of expertise? Contact Kaboer to discuss your PWB/PCB requirements and how our integrated approach can streamline your path to a successful, reliable product.
Kaboer manufacturing PCBs since 2009. Professional technology and high-precision Printed Circuit Boards involved in Medical, IOT, UAV, Aviation, Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Control, Artificial Intelligence, Consumer Electronics etc..