Date: 2025-12-19
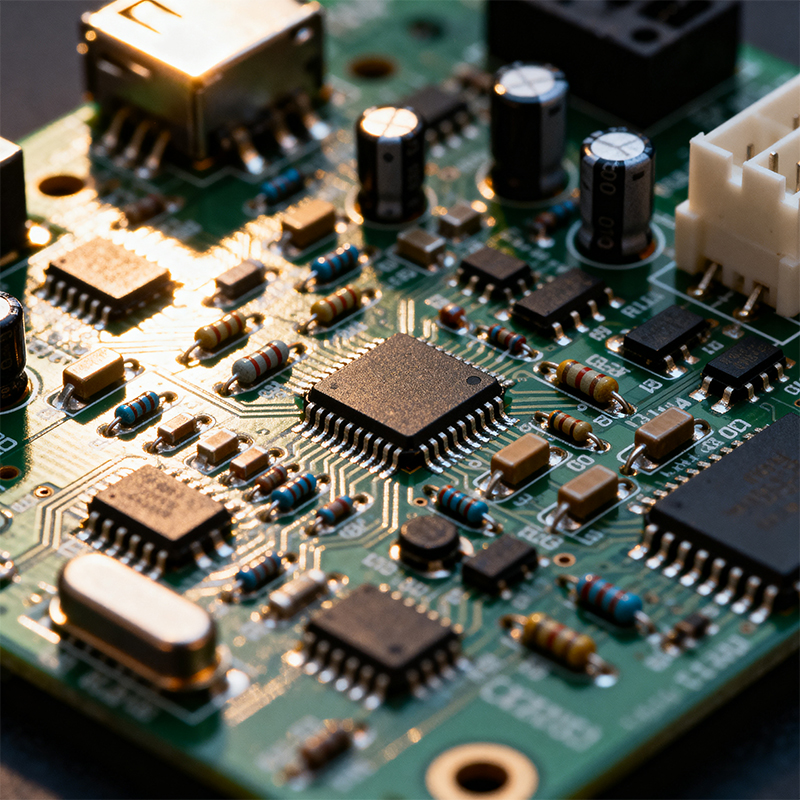
When designing or manufacturing electronic devices, understanding the parts on a circuit board is fundamental to creating functional, reliable, and cost-effective products. This comprehensive guide explores the essential components found on printed circuit boards (PCBs), their functions, and considerations for effective board design and assembly.
Resistors regulate current flow and divide voltages within circuits. Common types include:
Carbon film resistors: Economical general-purpose components
Metal film resistors: Better tolerance and temperature stability
Surface mount device (SMD) resistors: Miniaturized for modern electronics
Through-hole resistors: Traditional components for prototyping and high-power applications
Capacitors store and release electrical energy, filter signals, and stabilize power supplies. Key varieties include:
Ceramic capacitors: Small, stable, ideal for high-frequency applications
Electrolytic capacitors: Higher capacitance values for power filtering
Tantalum capacitors: Reliable, stable performance in compact packages
Inductors store energy in magnetic fields and filter high-frequency noise, while transformers transfer energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction.
ICs contain numerous microscopic components on a semiconductor chip, performing complex functions:
Microprocessors and microcontrollers: The "brains" of electronic systems
Memory chips: Store data and program instructions
Operational amplifiers: Amplify and condition analog signals
Application-Specific ICs (ASICs): Custom-designed for particular applications
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only, serving functions like:
Rectification: Converting AC to DC
Signal demodulation: Extracting information from carrier waves
Voltage regulation: Zener diodes maintain constant voltage
Light emission: LEDs for indicators and displays
As the fundamental building blocks of modern electronics, transistors amplify and switch electronic signals:
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs): Current-controlled amplifiers
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs): Voltage-controlled devices with high input impedance
MOSFETs: Dominant in digital circuits and power applications
Connectors provide removable interfaces between the circuit board and external devices:
Board-to-board connectors: Stack PCBs in compact arrangements
Wire-to-board connectors: Attach cables to the PCB
Input/output ports: USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and other standard interfaces
Switches manually control circuit connections, while relays use electrical signals to control other circuits, often isolating high-power loads from control electronics.
These components convert physical phenomena into electrical signals:
Temperature sensors: Thermistors, RTDs, and integrated sensor ICs
Motion sensors: Accelerometers and gyroscopes
Environmental sensors: Detect humidity, pressure, or specific gases
Maintain stable voltage levels despite input variations or load changes:
Linear regulators: Simple, low-noise, but less efficient
Switching regulators: More efficient but electrically noisier
Protect circuits from overcurrent conditions and voltage spikes:
Resettable fuses (PTCs): Automatically restore operation after fault conditions
TVS diodes: Divert voltage surges away from sensitive components
Substrate material: Typically FR-4 fiberglass, but ceramics, flex materials, or specialized laminates for particular applications
Copper traces: Conductive pathways connecting components
Solder mask: Insulating layer that prevents accidental shorts
Silkscreen: Text and symbols identifying components and test points
Standoffs and spacers: Physically support and separate boards
Heat sinks: Dissipate thermal energy from high-power components
EMI shields: Contain electromagnetic interference
Electrical specifications: Voltage, current, frequency, and power requirements
Physical dimensions: Package size and height constraints
Environmental factors: Temperature range, moisture resistance, and vibration tolerance
Cost and availability: Balancing performance with budget and supply chain considerations
Signal integrity: Minimizing trace lengths for high-speed signals
Thermal management: Arranging components to facilitate heat dissipation
Manufacturability: Organizing components for efficient automated assembly
Testability: Providing access points for debugging and quality verification
Electronic component shortages, obsolescence, and counterfeit parts represent significant risks to manufacturing continuity.
Unverified components may fail prematurely or perform outside specifications, risking product reliability and safety.
High-density component placement can create localized hot spots, reducing reliability and lifespan.
Poor component placement or selection can lead to crosstalk, electromagnetic interference, and circuit malfunction.
Successfully integrating diverse parts on a circuit board requires not only design expertise but also practical manufacturing experience. At Kaboer, we've refined our PCBA manufacturing processes to address the exact challenges mentioned above.
Strategic Component Sourcing: Based in Shenzhen, China—the global electronics manufacturing hub—we maintain strong relationships with component suppliers and distributors, helping clients navigate supply chain challenges and identify suitable alternates when necessary.
Comprehensive Verification Processes: We implement rigorous component inspection protocols, including visual checks, automated optical inspection (AOI), and X-ray verification for BGA components, to minimize the risk of counterfeit or substandard parts affecting your products.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Analysis: Our engineering team reviews component selection and placement early in the design phase, providing actionable feedback to optimize thermal performance, signal integrity, and ultimately, manufacturing yield.
End-to-End PCBA Solutions: From component procurement and precise SMT assembly to thorough testing and final packaging, we manage the complete manufacturing process in our own factory, ensuring quality control at every stage.
Whether you're prototyping a new design or scaling production for market launch, understanding the parts on a circuit board is only the first step. Partnering with an experienced manufacturer like Kaboer transforms that knowledge into reliable, high-performance electronic products.
The parts on a circuit board work in concert to create functional electronic systems. Each component—from the smallest resistor to the most complex microprocessor—plays a specific role in the overall circuit operation. Successful product design requires not only selecting the right components but also understanding how they interact physically and electrically on the PCB.
By mastering component characteristics, placement strategies, and supply chain management, electronics manufacturers can create more reliable, efficient, and competitive products. This knowledge, combined with partnership with a skilled manufacturing provider like Kaboer, positions companies to succeed in today's demanding global electronics market.
Kaboer manufacturing PCBs since 2009. Professional technology and high-precision Printed Circuit Boards involved in Medical, IOT, UAV, Aviation, Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Control, Artificial Intelligence, Consumer Electronics etc..