Date: 2025-12-19
A prototyping board (also known as a prototype PCB, breadboard, or development board) is a foundational tool used to build, test, and validate electronic circuit designs before committing to full-scale production. It serves as the physical platform where engineers and designers integrate components, verify functionality, debug issues, and refine their concepts. Unlike final production PCBs, prototyping boards prioritize flexibility, rapid iteration, and cost-effectiveness for low-volume validation.
Purpose: Ideal for initial concept validation and educational use
Structure: Plastic board with interconnected spring-clip contacts
Advantages: No soldering required; completely reusable; rapid circuit changes
Limitations: Unsuitable for high-frequency or high-current circuits; mechanical instability
Purpose: Intermediate prototyping with semi-permanent connections
Structure: Rigid board with pre-drilled holes on standard grid patterns
Advantages: More reliable than breadboards; supports soldered connections; handles moderate complexity
Common Types: Single-sided, double-sided, and copper-clad variants
Purpose: Structured prototyping with predefined copper tracks
Structure: Perforated board with parallel copper strips running along one side
Advantages: Reduces wiring complexity; suitable for digital and analog circuits
Design Consideration: Requires strategic track cutting to isolate connections
Purpose: High-fidelity prototyping that closely resembles final production boards
Structure: Professionally manufactured boards with custom layouts
Advantages: Validates manufacturability; tests signal integrity and thermal performance; essential for complex designs
Manufacturing Methods: Quick-turn PCB fabrication with reduced lead times (often 24-72 hours)
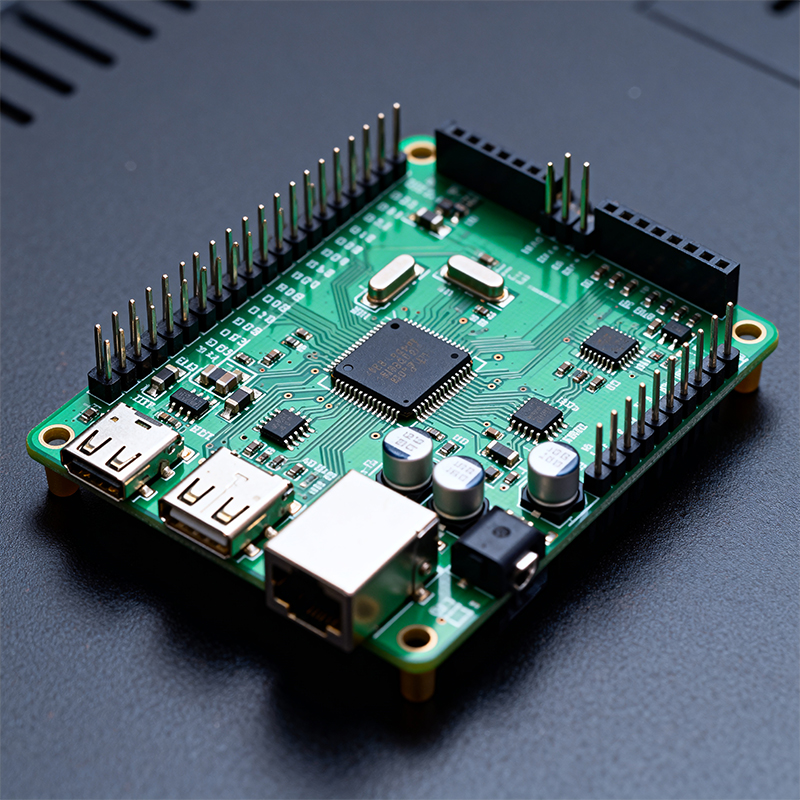
Purpose: Accelerated prototyping for specific technologies (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP32)
Structure: Integrated systems with pre-mounted processors, memory, and I/O interfaces
Advantages: Dramatically reduces development time; extensive community support
Application: Perfect for firmware development and proof-of-concept demonstrations
Low Complexity: Breadboards or perfboards suffice for simple circuits with under 20 components
Medium Complexity: Stripboards or small custom PCBs for analog/digital hybrid circuits
High Complexity: Custom prototype PCBs essential for BGA components, RF circuits, or impedance-controlled designs
Functional Testing: Basic prototypes that verify circuit operation
Performance Testing: Prototypes that must match final product specifications (speed, noise, power)
Environmental Testing: Prototypes subjected to thermal, vibration, or humidity conditions
Regulatory Testing: Prototypes used for EMC/EMI, safety, or compliance pre-certification
Rapid Iteration: Solderless boards allow immediate changes but lack production realism
Balanced Approach: Quick-turn PCBs offer reasonable speed with better fidelity
Cost Management: Budget allocation across multiple prototype revisions
Design for Manufacturability (DFM): How well the prototype informs production decisions
Component Sourcing: Whether prototype components match production availability
Scalability: Ease of transitioning from prototype to mass production
Tools: EDA software (Altium, KiCad, Eagle)
Output: Validated circuit schematic
Purpose: Theoretical verification before physical implementation
Decision Factors: Circuit complexity, testing needs, budget, timeline
Output: Selected prototyping methodology
Manual Assembly: Hand-soldering components for early prototypes
Machine Assembly: Automated pick-and-place for custom prototype PCBs
Output: Functional physical prototype
Electrical Testing: Voltage, current, signal integrity measurements
Functional Testing: Verifying all intended operations
Debugging: Identifying and resolving design flaws
Output: Refined, validated design
Iteration: Incorporating test findings into improved designs
Documentation: Recording all changes and test results
Output: Production-ready design files
Problem: Noise, crosstalk, or reflections in high-speed circuits
Solution: Use custom prototype PCBs with proper grounding and impedance control
Problem: Overheating components not apparent in simulation
Solution: Incorporate thermal testing early; use prototype PCBs with production-like thermal characteristics
Problem: Designs that work in prototype but can't be efficiently manufactured
Solution: Involve manufacturing expertise during prototyping phase
Problem: Prototype components differ from production versions
Solution: Source components through channels that reflect production supply chains
Problem: Multiple expensive prototype iterations
Solution: Strategic prototype planning; simulate thoroughly before building
Effective prototyping bridges innovative design with reliable manufacturing—a transition where many projects encounter difficulties. At Kaboer, we understand that a prototyping board is more than just a test platform; it's the critical link between concept and market-ready product.
Based in Shenzhen, China—the global epicenter of electronics manufacturing—Kaboer offers a seamless pathway from prototype to production:
Rapid Prototype PCB Fabrication
Quick-turn manufacturing (24-72 hours) for custom prototype PCBs
Support for complex requirements: impedance control, blind/buried vias, HDI designs
Material selection guidance for optimal performance and cost
Professional Prototype Assembly
Small-batch SMT assembly with the same precision as production runs
Comprehensive component sourcing, including hard-to-find parts
Mixed-technology assembly (SMT, through-hole, press-fit)
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Analysis
Early identification of production challenges while still in prototyping
Practical recommendations to improve yield, reliability, and cost-effectiveness
Smooth transition from prototype to mass production
Testing and Validation Support
In-circuit testing (ICT) and flying probe testing for prototype verification
Functional testing to ensure performance matches specifications
Environmental stress screening when required
Seamless Scaling to Production
Identical manufacturing processes from prototype through mass production
Consistent quality control across all volumes
Supply chain management that ensures component continuity
Whether you need a single prototyping board for concept validation or a batch of functional prototypes for field testing, Kaboer provides the manufacturing expertise to ensure your designs are not only functional but production-ready. Our integrated approach eliminates the gap between prototyping and manufacturing, giving you confidence that what works in prototype will work in volume production.
A prototyping board represents far more than a temporary test platform—it's an essential investment in product success. By selecting the appropriate prototyping strategy and partnering with a manufacturer that understands the complete development cycle, electronics companies can:
Reduce time-to-market through faster, more effective iterations
Minimize costly redesigns by identifying issues early
Ensure smoother transitions to mass production
Develop higher quality, more reliable products
In today's competitive electronics landscape, strategic prototyping isn't just an engineering phase—it's a business imperative that separates market leaders from the rest.
Kaboer manufacturing PCBs since 2009. Professional technology and high-precision Printed Circuit Boards involved in Medical, IOT, UAV, Aviation, Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Control, Artificial Intelligence, Consumer Electronics etc..