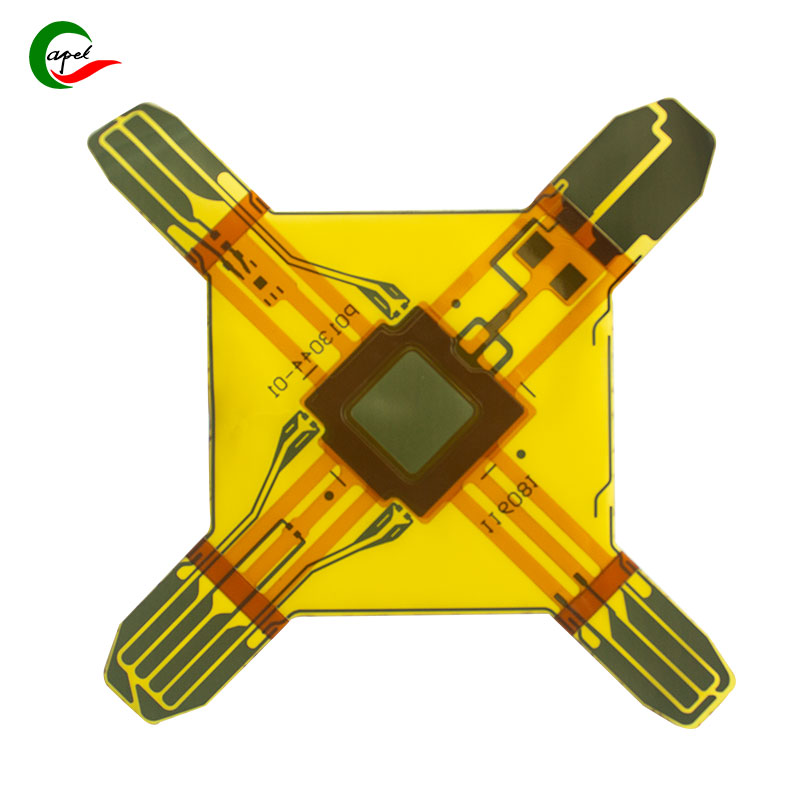
Multilayer flexible printed circuit boards (FPC PCBs) are critical components used in a variety of electronic devices, from smartphones and tablets to medical devices and automotive systems. This advanced technology offers great flexibility, durability and efficient signal transmission, making it highly sought after in today’s fast-paced digital world. In this blog post, we will discuss the main components that make up a multilayer FPC PCB and their importance in electronic applications.
1. Flexible substrate:
Flexible substrate is the basis of multilayer FPC PCB. It provides the necessary flexibility and mechanical integrity to withstand bending, folding and twisting without compromising electronic performance. Typically, polyimide or polyester materials are used as the base substrate due to their excellent thermal stability, electrical insulation, and ability to handle dynamic motion.
2. Conductive layer:
Conductive layers are the most important components of a multilayer FPC PCB because they facilitate the flow of electrical signals in the circuit. These layers are usually made of copper, which has excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. The copper foil is laminated to the flexible substrate using an adhesive, and a subsequent etching process is performed to create the desired circuit pattern.
3. Insulation layer:
Insulating layers, also known as dielectric layers, are placed between conductive layers to prevent electrical shorts and provide isolation. They are made of various materials such as epoxy, polyimide or solder mask, and have high dielectric strength and thermal stability. These layers play a vital role in maintaining signal integrity and preventing crosstalk between adjacent conductive traces.
4. Solder mask:
Solder mask is a protective layer applied to conductive and insulating layers that prevents short circuits during soldering and protects copper traces from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and oxidation. They are usually green in color but can also come in other colors such as red, blue or black.
5. Overlay:
Coverlay, also known as cover film or cover film, is a protective layer applied to the outermost surface of multi-layer FPC PCB. It provides additional insulation, mechanical protection and resistance to moisture and other contaminants. Coverlays typically have openings for placing components and allowing easy access to pads.
6. Copper plating:
Copper plating is the process of electroplating a thin layer of copper onto a conductive layer. This process helps improve electrical conductivity, lower impedance, and enhance the overall structural integrity of multilayer FPC PCBs. Copper plating also facilitates fine-pitch traces for high-density circuits.
7. Vias:
A via is a small hole drilled through the conductive layers of a multi-layer FPC PCB, connecting one or more layers together. They allow vertical interconnection and enable signal routing between different layers of the circuit. Vias are usually filled with copper or conductive paste to ensure a reliable electrical connection.
8. Component pads:
Component pads are areas on a multilayer FPC PCB designated for connecting electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors. These pads are usually made of copper and are connected to the underlying conductive traces using solder or conductive adhesive.
In Summary:
A multilayer flexible printed circuit board (FPC PCB) is a complex structure composed of several basic components. Flexible substrates, conductive layers, insulating layers, solder masks, overlays, copper plating, vias and component pads work together to provide the necessary electrical connectivity, mechanical flexibility and durability required by modern electronic devices. Understanding these major components helps in the design and manufacture of high-quality multilayer FPC PCBs that meet the stringent requirements of various industries.
Post time: Sep-02-2023
Back